
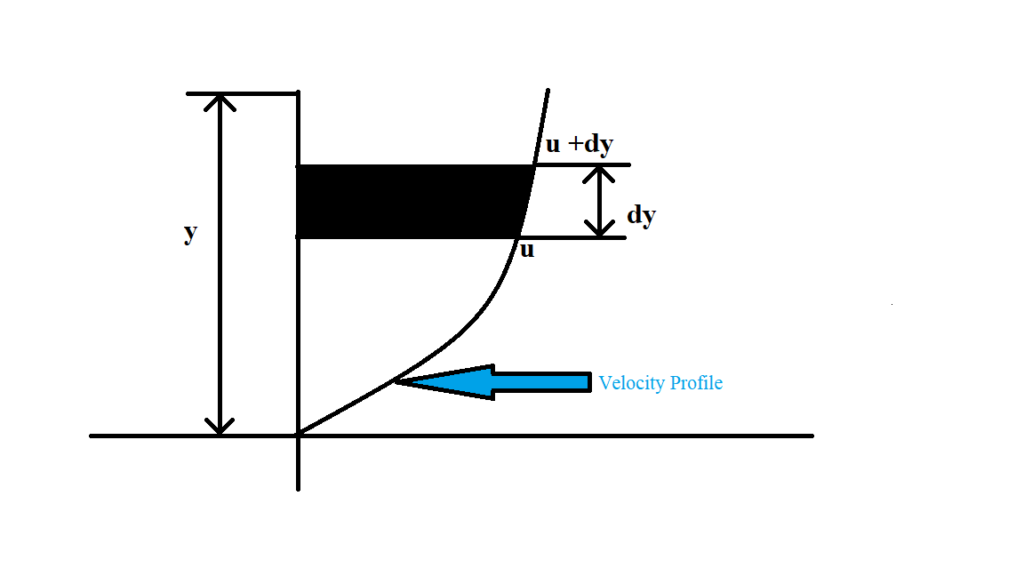

Shear stress in the fluid is possible due to the intermolecular friction exerted when layers of fluids attempt to flow over each other. When you need to determine the viscosity characteristics of a liquid which is not exposed to outside physical forces (in other words, when gravity is the only force acting on the liquid), kinematic should be the method of choice.The viscosity of a fluid is the measure of the resistance to its progressive deformation by traction or shear. In some cases, capillary-based instruments are more accurate for determining kinematic viscosity. However, it is simpler to use capillary-based instruments. Viscosity measurement for Newtonian fluids can be accomplished using rotational viscometers (via the conversion formula listed above). Some other products for which the kinematic method is suitable are blood and plasma, paints, polymers, and asphalt. With this information, changes in lubricating effectiveness can be evaluated. Using this testing method, changes in viscosity at different temperatures and under differing environmental conditions can be determined. Testing lubricating oils is a significant application. This measurement is used mostly for Newtonian liquids - liquids that do not change viscosity with changes in applied force (shear rate). Testing the product at different speeds will help provide guidelines for the design of the pumping system. Because the viscosity of non-Newtonian liquids changes with the speed of movement, pressure and pump velocity have serious impact on the specification of proper pumps, pressure and piping size. Testing the viscosity of the ketchup at different speeds (equating to different levels of force) will help ensure that the ketchup is behaving as it should.Īnother application is in the design of pumping systems. This product needs to have lower viscosity as it flows, to get it out of the bottle, but needs to be thick (or not as inclined to flow) when sitting on the burger. Non-Newtonian fluids are sensitive to changes in the amount of force exerted on them, and can sometimes even permanently change their viscosity if a constant force has been has been exerted on them over a period of time.Īn example of the importance of dynamic viscosity measurement is to indicate the proper flow characteristics of ketchup. These liquids are known as non-Newtonian fluids. The measurement of dynamic viscosity is most useful for liquids which change their apparent characteristics as force or pressure is applied. You test dynamic viscosity when you want to know the internal resistance of a fluid, or the force required to move one plane of the liquid over another. Density is not a factor with dynamic viscosity. This is because kinematic results are dependent on the density of the fluid. To further complicate my attempt to simplify these concepts, two fluids that have the same dynamic viscosity can have different kinematic viscosities. Put another way, kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. This is my attempt to bring clarity to these two principal concepts. It's not easy to find a lot of information on the differences between dynamic and kinematic viscosity. When people talk about viscosity, they are talking about one of two things: kinematic viscosity or dynamic viscosity. These terms are derived from how the viscosity is measured. In reality, there are several different terms that come under the heading of viscosity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
